Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China
2 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Science & Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
The optical Tamm state (OTS), which exists generally at the interface between metal and a dielectric Bragg mirror, has been studied extensively in the visible and near infrared spectra. Nevertheless, OTS in the terahertz (THz) region normally receives far less attention. In this Letter, we demonstrate the physical mechanism of OTS at the interface between graphene and a dielectric Bragg mirror in the THz frequency band by applying the transfer matrix method and dispersion characteristics. Based on such mechanisms, we propose an efficient method that can precisely generate and control OTS at a desired angle and frequency. Moreover, we show that the OTS is dependent on the optical conductivity of graphene, making the graphene–dielectric-Bragg-mirror a good candidate for dynamic tunable OTS device in the THz frequency range.
160.4236 Nanomaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(2): 020008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China
2 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Science & Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Materials and Devices, School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou 221116, China
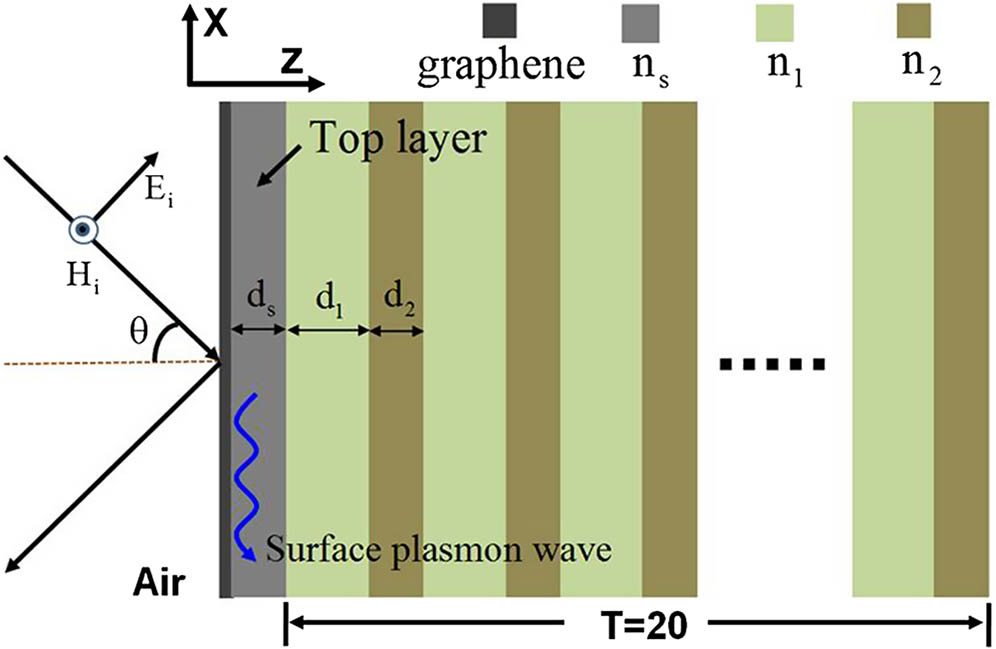
In this Letter, we have shown that a giant Goos–H nchen shift of a light beam reflected at terahertz frequencies can be achieved by using a composite structure, where monolayer graphene is coated on one-dimensional photonic crystals separated by a dielectric slab. This giant Goos–H nchen shift originates from the enhancement of the electrical field, owing to the excitation of optical Tamm states at the interface between the graphene and one-dimensional photonic crystal. It is shown that the Goos–H nchen shift in this structure can be significantly enlarged negatively and can be switched from negative to positive due to the tunability of graphene’s conductivity. Moreover, the Goos–H nchen shift of the proposed structure is sensitive to the relaxation time of graphene and the thickness of the top layer, making this structure a good candidate for a dynamic tunable optical shift device in the terahertz regime.
160.4236 Nanomaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(2): 020007
湖南农业大学植物激素与生长发育湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410128
经EMS诱变ag-10拟南芥后筛选获得一株矮化且叶色较深的突变体ah45,该突变体与ag-10相比具有开花时间晚,叶片更圆更小,果荚长度缩短,种子数目减少,生长周期延长等表型。遗传分析表明ah45的表型由隐性单基因突变所致。利用图位克隆的方法对突变位点进行初步定位,结果表明ah45突变基因位于第2号染色体的BAC克隆F5E13(1)与F6E13(2)之间61 kb区间内。
拟南芥 矮化 表型 遗传 Arabidopsis thaliana dwarf phenotype hereditary
湖南农业大学植物激素与生长发育湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410128
小麦籽粒中高分子量麦谷蛋白的含量与小麦的品质密切相关。通过Blast检索和生物信息学分析设计小麦高分子量麦谷蛋白亚基基因Dx5的特异引物, 以优质小麦济麦20基因组DNA为模板, 通过PCR扩增后测序, 获得长度为2 619 bp的序列。生物信息学分析表明其开放阅读框长度为2 520 bp, 编码839个氨基酸残基, 与GenBank数据库中的Dx5蛋白质一致性最高达到99%, 且具有高分子量麦谷蛋白亚基结构域。该序列命名为JMDx5, 提交GenBank数据库后被接收, 登录号为KJ144185, 为后续研究其表达机理及改良小麦品质奠定了基础。
小麦 高分子量麦谷蛋白亚基 生物信息学分析 wheat high molecular weight glutenin subunit Dx5 Dx5 bioinformatics analysis





